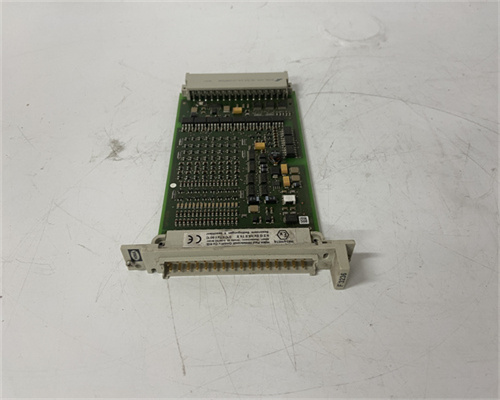
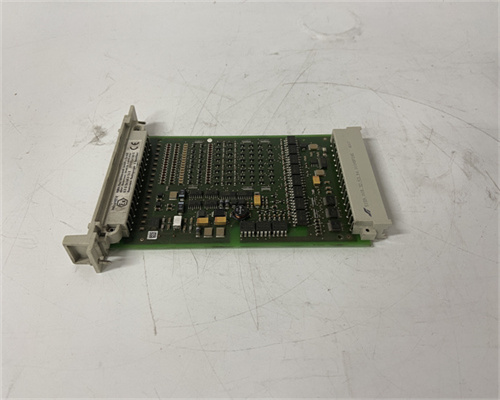
F3236
Function:
The HIMA F3236 is a high-performance safety relay designed for use in demanding safety applications within industrial automation systems. It acts as a critical component in a safety instrumented system (SIS), ensuring the safe operation of machinery and processes. Here's a breakdown of its key functions:
- Monitoring Safety Signals: The F3236 receives input signals from various safety sensors (e.g., light curtains, emergency stop buttons) that monitor the machine's operating state.
- Evaluating Safety Conditions: It compares these signals to pre-programmed safety parameters and evaluates if safe operating conditions are met.
- Initiating Protective Actions: If a safety hazard is detected (e.g., operator entering a restricted zone), the F3236 triggers immediate protective actions like shutting down the machine or stopping hazardous movements.
Possible Production Process:
Component Sourcing: HIMA likely sources various high-quality electronic components for the F3236:
- Microcontroller or safety processor for handling sensor signals, performing safety logic, and controlling outputs.
- Digital input and output modules for interfacing with safety sensors and actuators.
- Power supply circuitry to regulate power for different components of the relay.
- Communication interface circuitry (optional) to enable communication with a safety PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for system monitoring and diagnostics.
- Housing components designed for mechanical protection and heat dissipation within a control panel.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturing: The design is likely created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The PCB itself is fabricated according to the design, potentially involving multiple layers with etched circuitry and drilled holes for precise component placement.
PCB Assembly: Automated pick-and-place machines populate the PCBs with the procured electronic components. These components are then securely soldered onto the PCBs using reflow ovens or wave soldering techniques.
Software Installation: The F3236 likely requires pre-programmed firmware specifically designed by HIMA. This firmware contains the safety logic for evaluating sensor signals, implementing safety rules, and triggering protective actions.
Rigorous Testing and Quality Control: The assembled unit undergoes extensive testing to ensure proper functionality and safety:
- Functional testing to verify the relay's response to various safety input signals and its ability to initiate the programmed protective actions.
- Communication protocol testing (if applicable) to confirm accurate data exchange with a safety PLC.
- Environmental testing to ensure the unit can operate reliably within specified temperature and humidity ranges.
- Compliance testing to confirm adherence to relevant safety standards for functional safety (e.g., IEC 61508).
Packaging and Shipping: Once all tests are passed, the HIMA F3236 is labeled according to regulations and securely packaged for shipment to distributors or end users.
Materials and Manufacturing Technology:
- High-quality electronic components with extended lifespans suitable for demanding industrial environments.
- Lead-free soldering processes complying with environmental regulations (if applicable).
- Automated testing equipment for consistent quality control and safety assurance.
- Stringent manufacturing procedures to meet high safety integrity level (SIL) requirements.
Finding More Specific Information:
Obtaining extremely detailed information about the specific production process for the HIMA F3236 might be challenging due to proprietary manufacturing practices and the sensitive nature of safety-critical components. Here are some suggestions for further exploration:
HIMA Resources:
- Search the HIMA website for product manuals or data sheets related to the F3236 safety relay. These resources might provide details about its features, specifications, supported safety functions, and certifications for functional safety compliance.
- HIMA might offer application notes or technical documents that discuss safety relay selection, safety logic implementation, and integration of safety relays within safety instrumented systems.
Contact HIMA Directly: Reach out to HIMA's customer support or relevant department. They might be able to share general information about the F3236's functionalities but may not disclose confidential details about the production process due to its safety-critical nature.